Acute sinusitis
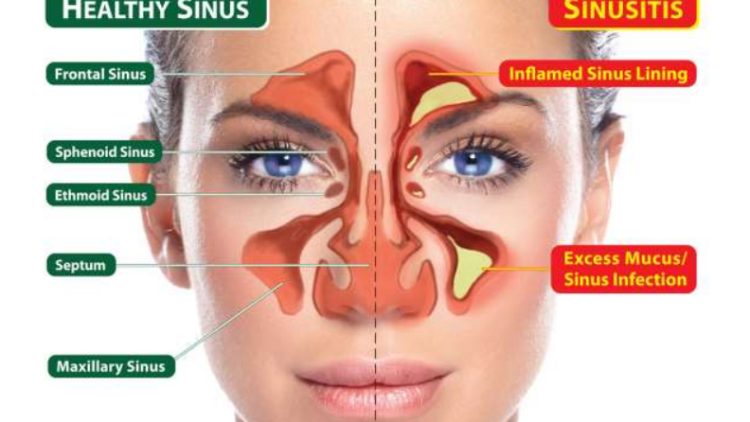
Acute sinusitis (acute rhinosinusitis) causes the cavities around your nasal passages (sinuses) to become inflamed and swollen. This interferes with drainage and causes mucus to build up.
With acute sinusitis, it may be difficult to breathe through your nose. The area around your eyes and face may feel swollen, and you may have throbbing facial pain or a headache.
Acute sinusitis is most often caused by the common cold. Other triggers include allergies, bacterial and fungal infections. Treatment of acute sinusitis depends on the cause. In most cases, home remedies are all that’s needed. However, persistent sinusitis can lead to serious infections and other complications. Sinusitis that lasts more than eight weeks or keeps coming back is called chronic sinusitis.
Symptoms
Acute sinusitis symptoms often include:
- Drainage of a thick, yellow or greenish discharge from the nose or down the back of the throat
- Nasal obstruction or congestion, causing difficulty breathing through your nose
- Pain, tenderness, swelling and pressure around your eyes, cheeks, nose or forehead
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- Cough, which may be worse at night Other signs and symptoms can include:
- Ear pain
- Headache
- Aching in your upper jaw and teeth
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Fatigue
- Fever
Treatments and drugs
Most cases of acute sinusitis don’t need treatment because they’re caused by viruses that also cause the common cold. Self-care techniques are usually the only treatment needed to speed recovery and ease symptoms.
Treatments to relieve symptoms
Your doctor may recommend treatments to help relieve sinusitis symptoms, including:
- Saline nasal spray, which you spray into your nose several times a day to rinse your nasal passages.
- Nasal corticosteroids. These nasal sprays help prevent and treat inflammation. Examples include fluticasone (Flonase), mometasone (Nasonex), budesonide (Rhinocort Aqua), triamcinolone (Nasacort AQ) and beclomethasone (Beconase AQ).
- Decongestants. These medications are available in over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription liquids, tablets and nasal sprays. OTC oral decongestants include Sudafed, Actifed and Drixoral. Nasal sprays include oxymetazoline (Afrin, others). These medications are generally taken for only a few days at most. Otherwise they can cause the return of more severe congestion (rebound congestion).
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others). Aspirin has been linked with Reye’s syndrome, so use caution when giving aspirin to children or teenagers. Though aspirin is approved for use in children older than age 2, children and teenagers recovering from chickenpox or flu-like symptoms should never take aspirin. Talk to
your doctor if you have concerns.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics usually aren’t needed to treat acute sinusitis.
- Antibiotics won’t help when acute sinusitis is caused by a viral or fungal infection.
- Most cases of bacterial sinusitis improve without antibiotics.
- Antibiotic treatment is generally needed only if the infection is severe, recurrent or persistent.
Antibiotics used to treat acute sinusitis caused by a bacterial infection include amoxicillin (Amoxil, others), doxycycline (Doryx, Monodox, others) or the combination drug trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, others). If the infection doesn’t go away or if the sinusitis comes back, your doctor may try a different antibiotic.
If your doctor does prescribe antibiotics, it’s critical to take the entire course of medication. Generally, this means you’ll need to take them for 10 to 14 days — even after your symptoms get better. If you stop taking them early, your symptoms may come back.
Antifungal medications
Rarely, acute sinusitis is caused by a fungal infection, which can be treated with antifungal medication. The dose of medication — as well as how long you’ll need to take it — depends on the severity of your infection and how quickly your symptoms improve.
Immunotherapy
If allergies are contributing to your sinusitis, allergy shots (immunotherapy) that help reduce the body’s reaction to specific allergens may help treat your symptoms.
Prevention
Take these steps to help reduce your risk of getting acute sinusitis:
- Avoid upper respiratory infections. Minimize contact with people who have colds. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before your meals.
- Carefully manage your allergies. Work with your doctor to keep symptoms under control.
- Avoid cigarette smoke and polluted air. Tobacco smoke and other pollutants can irritate and inflame your lungs and nasal passages.
- Use a humidifier. If the air in your home is dry, such as it is if you have forced-air heat, adding moisture to the air may help prevent sinusitis. Be sure the humidifier stays clean and free of mold with regular, thorough cleaning